Before writing a PostgreSQL query, we will create a scenario, suppose we have two tables first are Customer, and Second is its Orders. First, we will create tables through the following query then we will write the query to select the records that most recently ordered by a customer.
--Create Customer table CREATETABLEcustomer ( cust_idintgeneratedalwaysasidentity, nametext, phonetext ); --Create Order table CREATETABLEorders ( idintgeneratedalwaysasidentity, cust_idint, qtyint, pricedecimal, created_datedate ); --Let us insert some records in the customer table INSERTINTOcustomer(name,phone) VALUES('Dilip','9091228998'), ('Anil','9099887886'), ('Ashish','9801228990'); --Let us insert some records in the order table INSERTINTOorders(cust_id,qty,price,created_date) VALUES(1, 2, 10.00,'21/04/2020'), (2, 4, 30.00,'22/04/2020'), (3, 5, 60.00,'21/04/2020'), (1, 6, 10.00,'22/04/2020'), (2, 7, 30.00,'23/04/2020'), (3, 5, 90.00,'25/04/2020'), (2, 6, 86.00,'24/04/2020'); |
Using Lateral join we can find the expected result set.
Using LATERAL JOIN in PostgreSQL
SELECTc.cust_id,c.name,o.created_date,o.qty,o.price FROM customerc CROSS JOINLATERAL( SELECTo.created_date,o.qty,o.price FROM orderso WHERE o.cust_id=c.cust_id AND o.created_date<=current_date ORDER BYo.created_dateDESCNULLSLAST LIMIT 1 )o; |
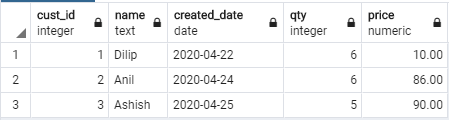
Result:
You can replace current_date with a parameter to get the records according to your desire date.